453 million tourism nights spent in the first quarter of 2023
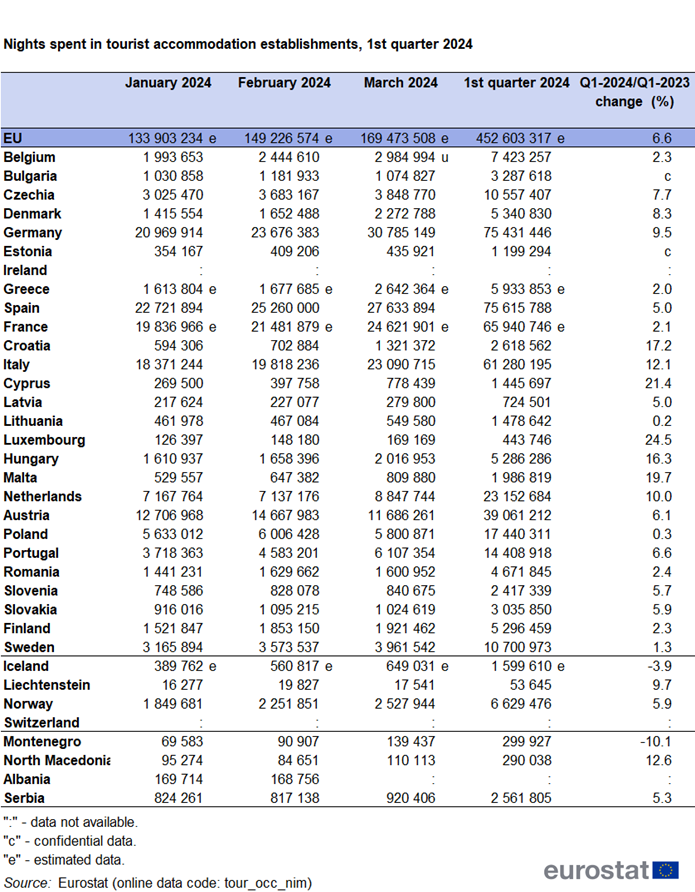
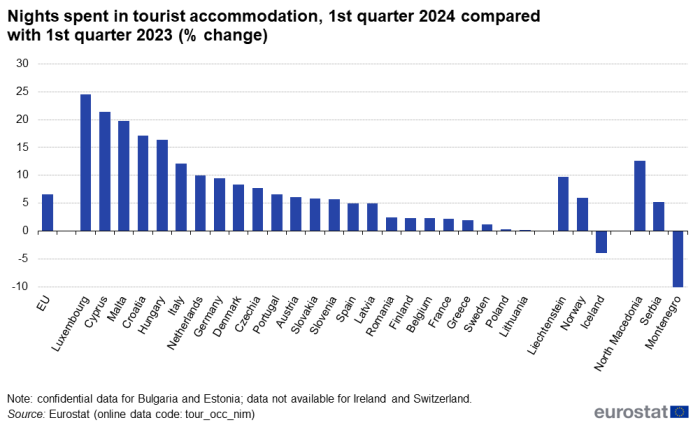
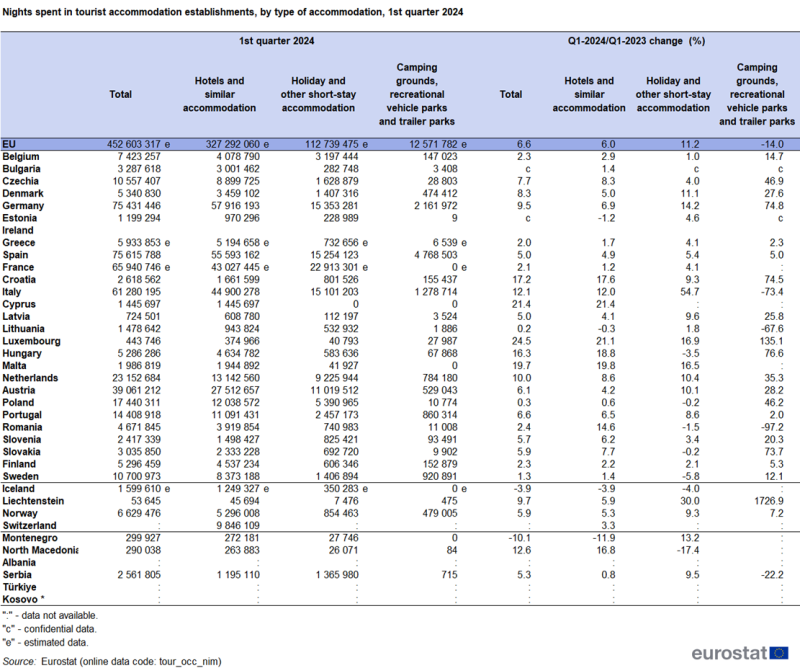
In the first three months of 2024, 452.6 million nights were spent in EU tourist accommodation (see Table 1). This corresponds to 27.8 million more nights (+6.6 %) than those spent in the first quarter of last year. All EU countries with available data reported positive trends, compared with the first quarter of 2023. The highest increases were recorded in Luxembourg (+24.5 %), Cyprus (+21.4 %), Malta (+19.7 %) and Croatia (+19.7 %) (see Figure 1). In absolute figures, the largest contributions to the overall increase with 27.8 million nights were observed in Italy (+6.6 million), Germany (+6.5 million), Spain (+3.6 million), Austria (+2.2 million) and the Netherlands (+2.1 million), jointly accounting for more than three-quarters of the increase in the EU.
In January, February and March 2024, the number of nights spent exceeded the figures of the corresponding months in pre-pandemic year 2019. The number of nights spent in the first quarter of 2024 increased by 24.5 million (+5.7 %) compared with the first quarter of 2019.
Source: Eurostat (tour_occ_nim)
Source: Eurostat (tour_occ_nim)
Double-digit increase of international tourism in the first quarter
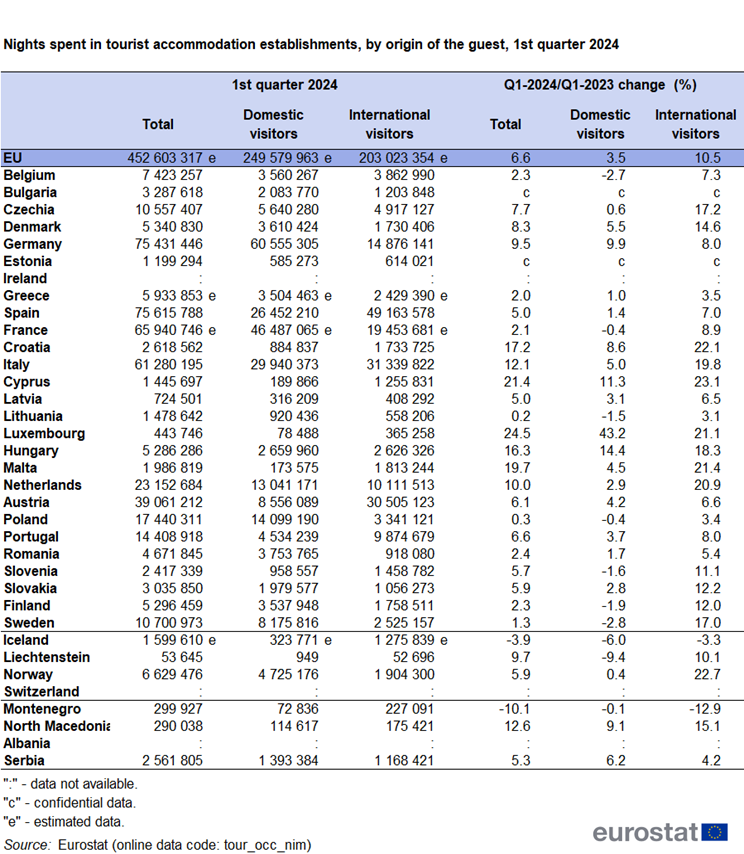
Looking at the breakdown by origin of the guest, in the first quarter of 2024, compared with the first quarter of 2023, international tourism (+19.3 million nights, +10.5 %) contributed more to the overall increase of nights spent than domestic tourism (+8.5 million nights, +3.5 %) (see Table 2).
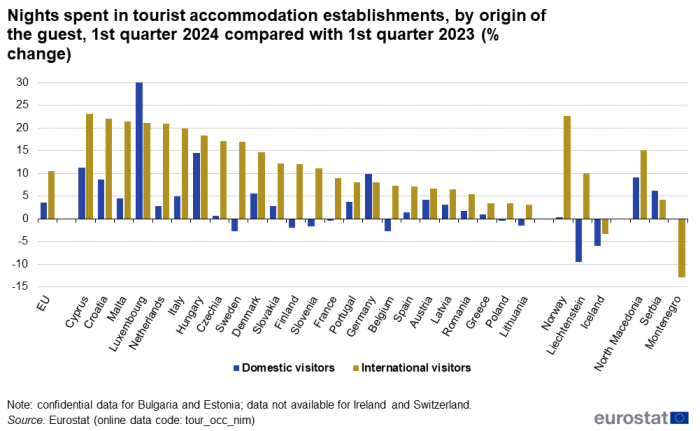
In the first quarter, international tourism increased particularly strongly, by more than 20 %, in Cyprus (+23.1 %), Croatia (+22.1 %), Malta (+21.4 %), Luxembourg (+21.1 %) and the Netherlands (+20.9 %) (see Figure 2). More than half of the international nights spent in the first quarter (111.0 million out of 203.0 million) were observed in Spain (49.2 million, accounting for nearly 1 in 4 international nights), Italy (31.3 million) and Austria (30.5 million). An increase in international tourism was also observed in all other EU members for which data is available.
In absolute terms, domestic tourism was the predominant contributor (249.6 million nights) to the 452.6 million nights spent in tourist accommodation across the EU in the first quarter. Between January and March, 60.6 million nights were spent in Germany by residents of that country (+9.9 % compared with the first quarter of 2023). France recorded 46.5 million nights spent by residents, a small decrease (-0.4 %). In six more EU countries (out of 24 with available data), the number of domestic tourism nights was lower in the first quarter of 2024 than in the same period in 2023.
Source: Eurostat (tour_occ_nim)
Source: Eurostat (tour_occ_nim)
18 million more hotel nights in the first quarter
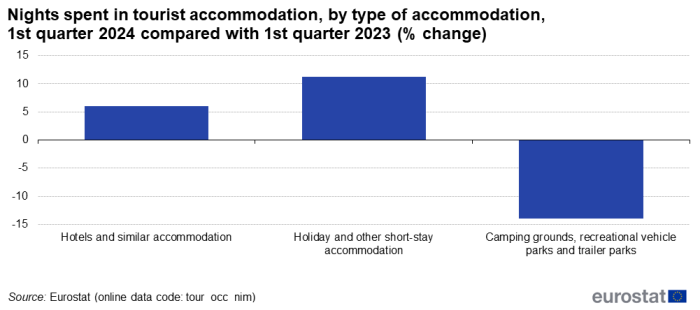
Two of the three types of tourist accommodation showed increases for the first quarter compared with the same period in 2023 (see Table 3). The segment of hotels and similar accommodation showed the highest increase in absolute terms, up by 18.5 million nights (+6.0 %). This segment accounted for 72.3 % of tourist accommodation. Nights spent at holiday and other-short stay accommodation (representing 24.9 % of the tourist accommodation market) increased by 11.2 %, the smaller segment of campsites decreased by 14.0 % (but in the winter months January, February and March, campsites only account for 2.8 % of all nights spent). An important part of the 12.6 million nights spent at campsites were recorded in Spain (4.8 million).
Source: Eurostat (tour_occ_nim)
Source: Eurostat (tour_occ_nim)
Data on tourism nights is included in the interactive European Statistical Recovery Dashboard, which contains monthly and quarterly indicators from a number of statistical areas relevant for tracking the economic and social recovery from the Covid-19 pandemic, across countries and time. The dashboard is updated every month with the latest available data for each indicator.
Source data for tables and graphs
Data sources
This article presents the short-term trends in nights spent in tourist accommodation in the EU, analysing monthly data provided by Member States.
For the year-to-year evolution of the number of nights spent in tourist accommodation and a detailed analysis of 2022 annual data, see Tourism statistics – annual results for the accommodation sector.
Context
The EU is a major tourist destination, with four Member States among the world’s top ten destinations for holidaymakers, according to UNWTO[1] data. Tourism is an important activity in the EU which contributes to employment and economic growth, as well as to the development of rural, peripheral or less-developed areas. These characteristics drive the demand for reliable and harmonised statistics on this activity, as well as within the wider context of regional policy and sustainable development policy areas.