In the third quarter of 2023, in the EU, the share of part-time workers among employed women aged 15-64 (28%) was higher than the share of men (8%). Women registered higher share of part-time employment in all occupational categories as defined by International Standard Classification of Occupations (ISCO).
The largest difference between the shares of women and men part-time workers was reported in the category elementary occupations, referring to helpers, cleaners or food preparation assistants. The difference was 29 percentage points (pp), with 47% of women employed as part-time workers and 19% men. Among service and sales workers, 35% of women were employed part-time, compared with 16% of men. Among clerical support workers, 29% of women were employed part-time and 9% of men.
The lowest differences between the shares of part-time workers were registered among the managerial occupations (10% women vs 3% men) and plant and machine operators and assemblers (12% vs 4%).
Source dataset: lfsq_epgais
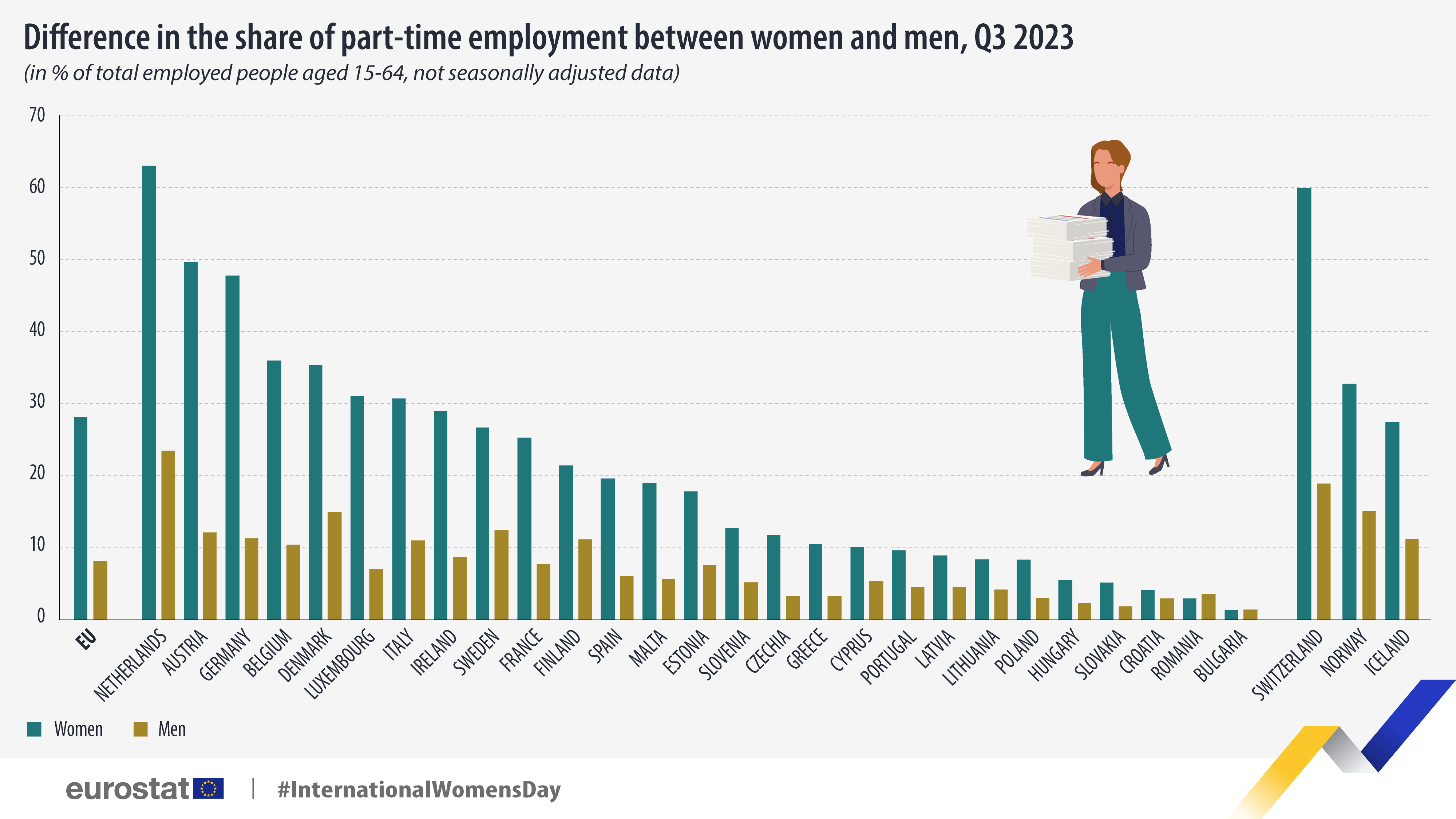
In most EU countries, women had a higher share of part-time workers. The Netherlands recorded the highest share of women working part-time, 63% of total employment compared with 23% for men, and the largest difference between women and men (39 pp). Large differences between women and men were also recorded in Austria (38 pp) and Germany (37 pp).
Romania was the exception, with the share of men employed part-time (4%) slightly higher than that of women (3%). In Bulgaria, women and men registered equal shares of part-time employment (1% for both categories).
Source dataset: lfsq_epgaed
This article is part of a series of articles published to mark International Women’s Day.